If you’re associated with SEO, digital marketing, or even managing online marketing for your business, chances are you’ve been befuddled by the use of the term RankBrain. Now, you need to what it truly means, and whether it actually has an impact on your business.
Here’s the Bloomberg news piece that revealed RankBrain to the world. We recommend you watch the video embedded in the page.
We will cover all the basics, as well as the advanced and intricate bits of RankBrain in this guide.
Note: Google has been highly secretive about RankBrain, so there’s not a lot of official information you’ll find about this online. That said, we’ve conducted focused experiments, and consumed every credible source of information to create this Rank Brain guide.
The Basics of RankBrain
RankBrain is an AI-powered search engine algorithm that Google has now officially confirmed it’s using to help sort and prioritize online rankings.
RankBrain has technically been in use since 2015, but at that time it was only affecting about 15% of Google’s total search queries. Fast forward to Rankbrain 2019 and this ‘smart’ AI sorting system is now an integral part of Google’s search algorithm and drives a majority of Googles searh results.
The global tech narrative has shifted and the idea of AI-based technology seems almost commonplace at this point. It should come as no surprise that Google would be at the forefront of this moment. In fact, only a year after its official confirmation of the use of AI, news came out that Google was using RankBrain for all its 2 trillion search queries.
Note: Several SEO ‘experts’ call RankBrain ‘Google’s search algorithm’. That’s not exactly true, because the comprehensive search algorithm is called Hummingbird, and RankBrain is its AI-powered component.

What does RankBrain do?
The simple answer – offers better search results.
The longer answer is as follows.
RankBrain:
- Makes Google’s search algorithm smart enough to understand patterns in user search and browsing behavior
- Learns from these patterns
- Uses what’s learned to decide on quantifiable changes in its working procedure
- Measures the impact of the changes
- Builds upon this measurement to either do more of the same (until it identifies the ‘sweet spot’) or reverts the changes if the results are not as expected.
*sweet spot: when incremental additions in the independent variable don’t lead to expected improvements in the dependent variable.
Examples of RankBrain At Work
While it’s not possible to isolate RankBrain’s impact on search results for a query, there are several examples on the web that try to showcase how the AI component of Google’s algorithm is trying to make more sense of search queries than was previously possible.
This ideology of leveraging deep learning and Natural Language Processing is substantiated with official releases from Google on its blog.
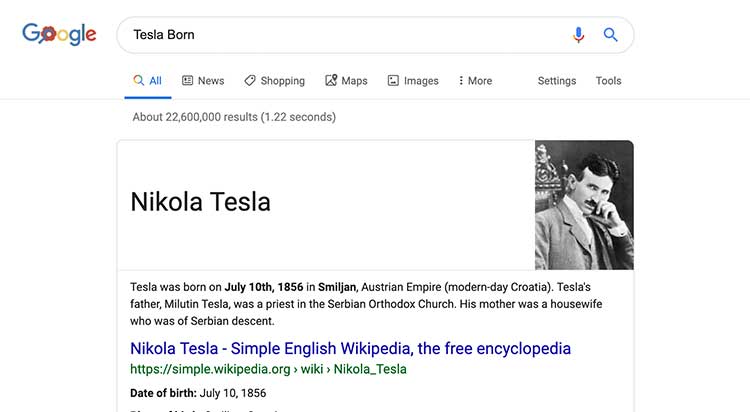
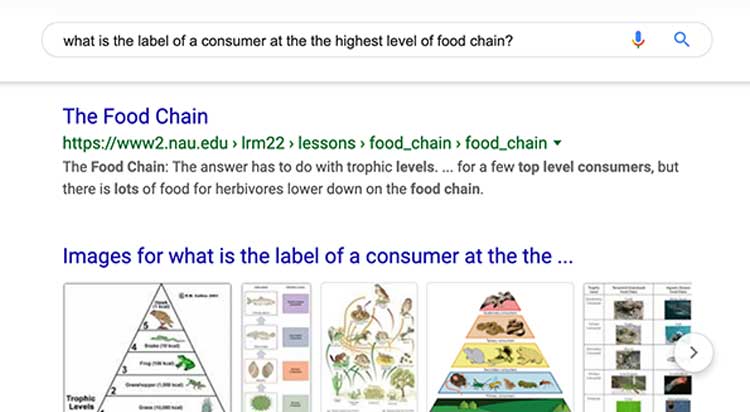
Consider this example of how RankBrain enables Google to make sense of seemingly ambiguous and verbose search queries.
Here’s an example of RankBrain differentiating between different user intent based on just a single word variation in a search query.
Case 1:
Google determines the user is interested in knowing when the inventor Nikola Tesla was born
Case 2:
Yet with another similar query, Google understand that the search intention is different than the previous example and it adapts its results based upon this understood intent.
How do we know RankBrain is the way forward for Google?
Well, Google has revealed that in a comparison between Google’s engineering team and RankBrain, the latter outperformed the former by 10%, when it came to picking the best search results for specific queries.
Also, Google has revealed that RankBrain is the third most important ranking factor for websites, after content and backlinks.
These two revelations are proof enough that RankBrain is truly in-play, and is a vital part of Google’s present and future plans for its search engine.
How Does RankBrain Understand Whether Users Are Satisfied With A Search Result?
Again, Google has never released official notes about this (nor is it expected to, ever). However, all machine language applications, in principle, define ‘concepts’ based on user behavior and then devise meaningful KPIs to quantifiably measure those concepts.
In RankBrain’s case, the user satisfaction is judged based on how the algorithm defines related user metrics, and how it distills them into KPIs.
The internal terminology used in Google will certainly be different, but these concepts are closely related to:
- Organic Click-Through-Rate
- Dwell Time: the total time a user spends on a specific search result before coming back to the results page
- Bounce Rate: a measure of stickiness (or the lack of it)
- Pogo-sticking: the act of a user quickly browsing through search results sequentially, and then finally spending a significantly larger amount of time on a particular page (which tells Google that this page solved the user’s query the best)
What Does This Mean for SEO?
A lot. And it’s highly abstract, not easy to quantify and isolate from the core concept that has traditionally driven SEO.
That said, here are the 3 key takeaways for anybody interested in understanding the ‘directional’ changes that RankBrain is bringing to SEO.
1. Different types of search queries equate to different ranking signals indicators
There are more than 200 different ranking factors that Google uses to prepare its search results for different queries.
RankBrain is making HummingBird even smarter
RankBrain is now making HummingBird (A 2013 Google algorithm update) smart enough to know which signals to bring in play for which kind of search queries. For example:
- A news related search query may value freshness more than link diversity and keyword matching
- For a subject matter related query, authority signals will outplay others such as social shares
- For a local business search, user reviews and ratings and number of citations will play a higher role than keyword match/content authority
The takeaway for SEO: understand the intent for which you are trying to rank a website/webpage and then design your SEO strategy accordingly.
2. Rankbrain Knows What Your Website Is About
Essentially, RankBrain is trying to contextualize all information on the web, contextualize the user’s search query and then create well-informed matches based on that relationship.
So, now’s the time for you to start working on your website’s ‘context’. Understand that HummingBird understands that Quora is the dependable source of answering questions, Amazon is the right destination for someone trying to shop for stuff online, Yelp is what’s going to suit someone hunting for information on local business, and Reddit is where the users go for trending news, information and networking.
Ask yourself – what’s my website’s (or my clients’ websites’) context? Then, design your SEO strategy around this desired context.
For a local business website, generating online reviews, optimizing keywords for voice search, expanding the range of online citations, etc. is going to pay off much sooner than trying to build authority over a subject matter.
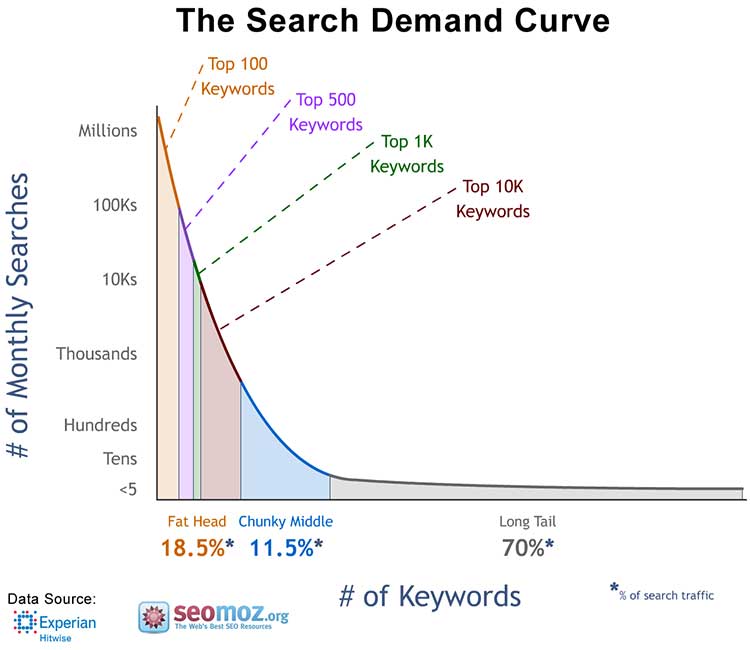
3. Stop chasing single-word keywords
Long-tail keywords comprise 70% of web searches. Anybody who’s been following SEO trends for the past few years probably already knows this.
Here’s some extensive research that showcases the effectiveness of long-tail keywords compared to single word keywords.
This means the traditional SEO practice of ‘one page, one keyword’ is dead.
How to Attune Your SEO With RankBrain?
This is probably the most important question you can ask post RankBrain!
A couple of strategies you’d want to get started with are:
1. Medium tail + long tail + LSI + question based keywords
Writing page titles, meta descriptions, and page content around a single keyword is not going to get your SEO anywhere. There are probably tens of thousands of websites doing that already.
You will be able to build a reputation and communicate your website’s relevance for a subject by optimizing your keyword research around the 4 ideas mentioned earlier.
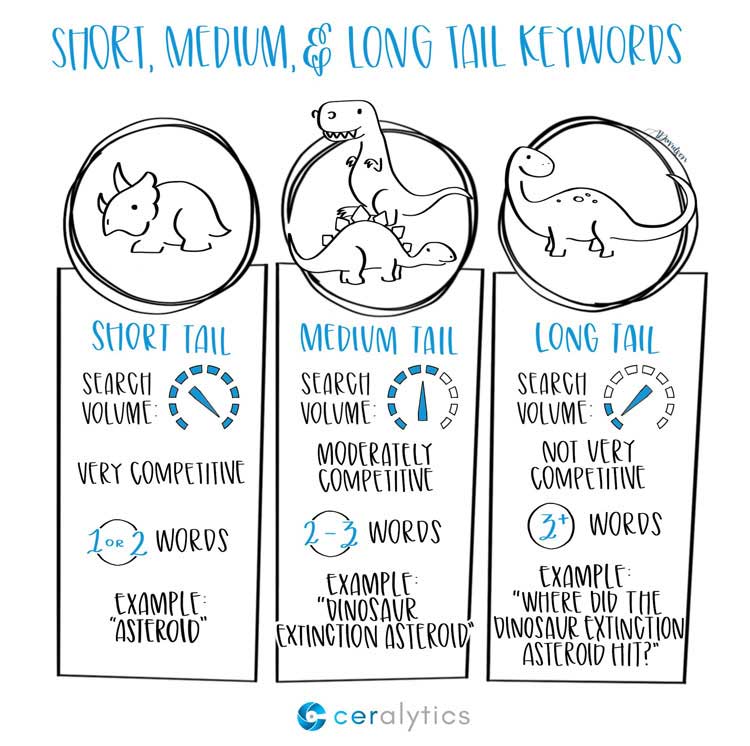
Long-Tail Keywords
We already explained how important it is. Get started with keywordtool.io, a free tool to help you generate long-tail keywords.
Medium Tail Keywords
As more and more websites start optimizing their content around long-tail keywords, the next wave of filtering is bound to happen. RankBrain will try to categorize websites into different segments, based on their levels of authority and relevance.
To beat the competition, you will also need to include medium tail keywords (2-3 words long) in the mix.
This means your websites will target search queries that have traffic higher than long-tail keywords, but competition lower than short (1-word) keywords.
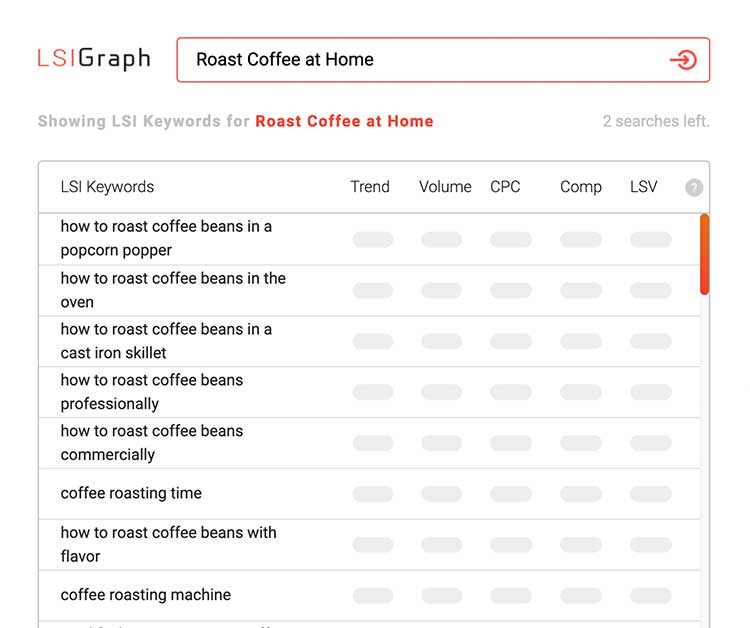
LSI (latent semantic indexing) keywords
When you’re creating that ambitious 10,000+ word skyscraper blog post to tell Google who is boss, you will come short-sided if you are not focusing on seasoning your content with semantically related words!
Use LSI Graph a free tool to generate LSI keywords
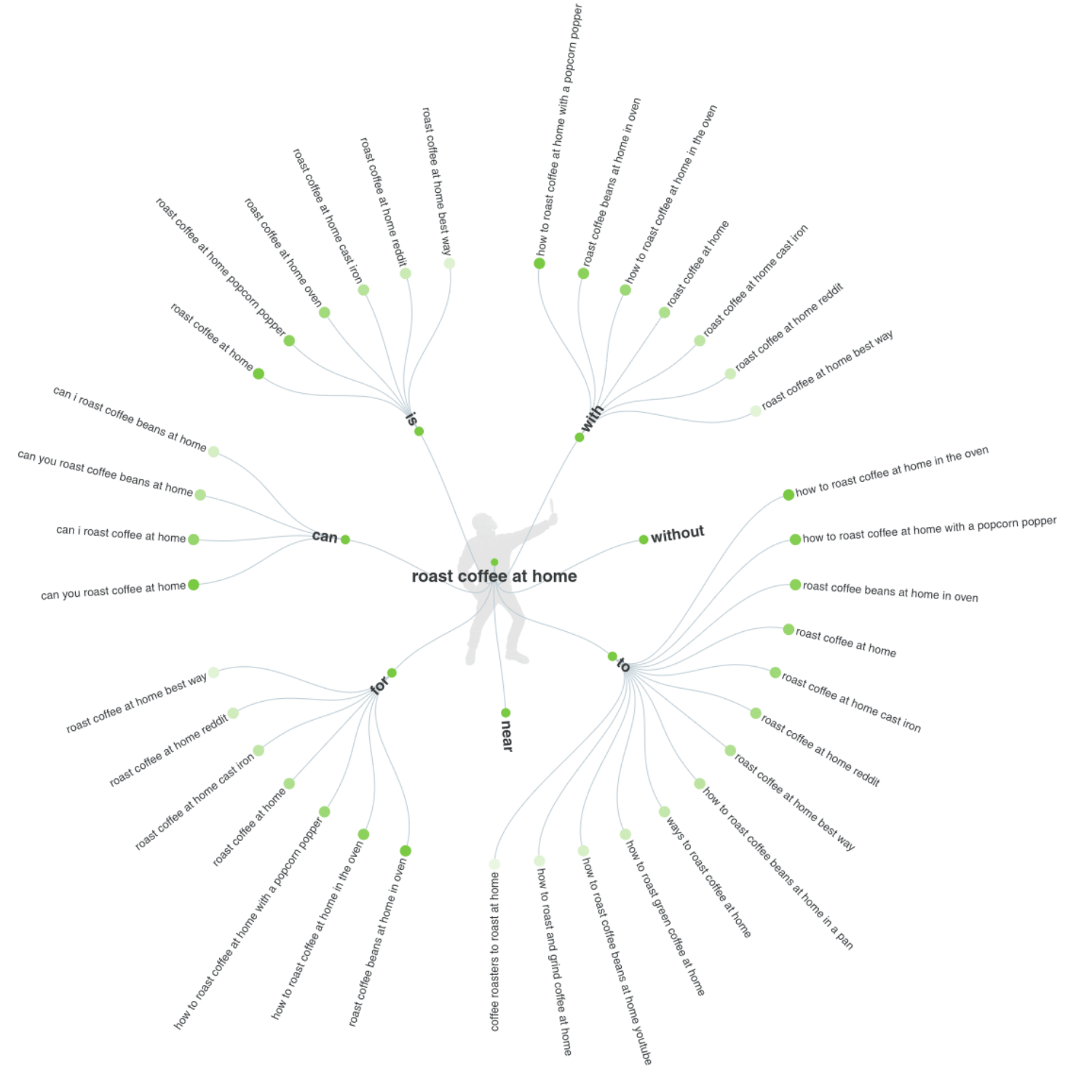
Question Keywords
Did you know – 20% of voice search queries are triggered by combinations of these 25 words!
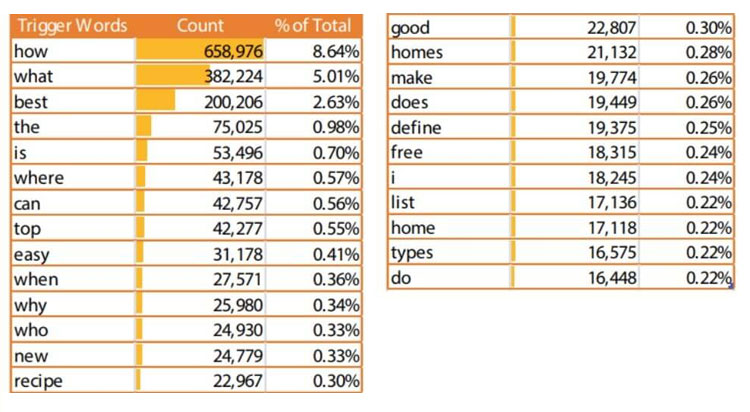
Question-based keywords are going to become more popular with time, as voice search expands its base, and smart speakers and voice assistants proliferate across global markets.
A superb free tool you can use to get started – AnswerThePublic.
2. Optimize Your Content to Maximize Dwell Time and Minimize Bounce Rate
How do you do that: Try these tactics.
1. Get your main content above the fold.
Remove pop-ups from your page. Don’t let header images make it mandatory for users to scroll down midway to get some meaningful content.
2. Prepare detailed guides.
Obviously reading 3,000 words is going to take a lot of time, as compared to a 300 word page. This can do a world of good to your page’s Dwell Time.”
3. Divide your content into several small bite-sized chunks.
The psychological factor at play here is – your readers get the sense of a mini victory as they skim each section of your content. Check out the top 3 results you get on Google for the next informational searches you do. Chances are the pages are divided into dozens of small blocks. Do that.
Conclusion
RankBrain – you’ll continue to hear a lot about it. This machine learning infrastructure is now an integral part of Google’s comprehensive web search algorithm. Also, slowly and steadily, the principles behind the working of RankBrain have come out in the open.
Now, rather than waiting for ‘concrete’ or official information from Google, it makes sense to understand the principles and evaluate how you can optimize your website and re-invent your SEO strategies to ensure it matches well RankBrain.
Voice SEO, local SEO, natural language processing, machine learning, artificial intelligence – all these constructs come together and culminate into exactly what RankBrain intends to do. That is, show users the search results that solve their problems, answer their questions, tell them ‘how to do it’, direct them ‘where to buy it from’, and instruct them what to do next.