Ever wondered what on-page SEO Techniques actually work and what ones don’t?
 For example, do SEO Techniques like using your target keyword in your URL really have an effect on your SEO? Does your website load time really factor into how your website ranks? These suggestions and those like it are often the kind of things you will hear online but do they really work?
For example, do SEO Techniques like using your target keyword in your URL really have an effect on your SEO? Does your website load time really factor into how your website ranks? These suggestions and those like it are often the kind of things you will hear online but do they really work?
In this post, we look at some of the top on-page SEO techniques recommended by the pros evaluating each for their effectiveness.
Listen to The Audio Version
Use short URLs for your pages.
Ex. website.com/local-seo
So true or false do short URLs rank better in Google? A recent study of on-page SEO factors shows that on average short URLs with about 17 or so characters ranked visually better than longer ones. So there is some precedent to utilizing shorter URLs.
Does this mean you should go an change all of your long URLs to shorter ones? Probably not. Even though there is a slight correlation between better rankings and shorter URLS is not likely significant enough to go through and update all of your websites URLs. Just know that going forward shorter URLs are better than longer as it relates to ranking in Google.
Use your primary keyword in your URL.
If I were writing an article about SEO tips, then my final URL with my keyword target might look like this. https://website.com/seo-tips
So does this actually help you rank higher on Google? – The answer is false
Out of all of the keyword related to on-page SEO factors in this post this was one of the only ones that showed a negative correlation. Even John Muller from Google has stated that this is only a very small SEO factor.
So do we still recommend using it? – Yes
Why because when your links get shared people can easily identify what the page is about before ever clicking through to the page. This often increases referral traffic compared to links that are more ambiguous.
For example, look at the two URLs below. Which one provides more context?
website.com/2019-#1298.html
website.com/my-trip-to-burningman
The second reason is we still suggest this is the exact match keyword that you want to rank for will be included in the anchor text of the every naked URL backlink that you get.
Ex. website.com/my-target-keyword
Recent studies have shown that top ranking pages tend to have a larger percentage of exact match anchor text links in their backlink profile.
So when creating new content its worth your time to customize your URLs and reap the benefits.
Use your keyword in the headline.
Placing your keyword in your H1 tag is a is a common practice in SEO but does it really make a difference?
One study found that about 85% of the pages that rank in the top 10 of Google don’t have their keyword in their H1 tags.
But there is still a small correlation so we still recommend this practice. The main reason for this is more user experience based. One study from Nielsen Norman Group found that…
On average Web pages, users only read at most 28% of the copy on a page.
Scanning text is an extremely common behavior for users. You have probably looked through a page online scrolled for a while and if something caught your eye you read that portion. If you find that section engaging you might then scroll back up to recap what you missed.
Using keyword related text in headings and subheadings may be enough to peek a users interest and keep them on your page longer.
Adding external links to authoritative websites.
While Google’s John Muller said that adding external links to other sites is not a ranking factor in Google’s Algorithm yet a study from Reboot online disagrees.
They did an experiment on two completely made up terms. They set up 10 different websites, 5 that linked to authoritative sources and then the other 5 had no external links. The result of their study was clear. Site with external links ranked higher than the ones that did not.
So the takeaway is not to be afraid to link out to an authoritative website that enhances the user experience.
Adding internal links to pages that you want to rank.
Internal links are links that go from one page on your site to another page on that same site. These have been proven time and time again to help with your websites rankings.
One quick tip is to find pages on your site that currently ranking on page 2 of Google. Add some internal links from other relevant pages and in time you might notice that this passes enough link juice to boost the target pages rankings.
Re-optimizing titles on underperforming pages.
Even if you have the perfect title and meta description this won’t really matter much unless you are on page one of Google? Why? Because as the saying goes…
The best place to hide a dead body is on page 2 of Google.
To fix pages with poor rankings you need to first identify these pages. You can do this via Google search console.
We did a step by step of this processes on how to do meta-tags-seo
If you have pages that are below position 3 then modifying and testing your meta title and descriptions might be just the thing to improve your click-through rate and as a result your rankings.
One way to get ideas for great titles is to do Google searches around your keyword. Scan the results to see if there are any trends across all the SERPs that you might want to incorporate into your pages title and meta description updates.
Also, pay attention to the paid listings in those search results. Since advertisers pay less money per click when their ads have a better performing click through rate, you can wager that many of the ad spots that show up for your target keyword search have been tested for copy that gets better than average results.
Long form blog post.
People have been talking about long-form content for quite a while now and authorities in the industry like Neil Patel write about this often.

Even today this still seems to be a viable technique for improving your on-page SEO .
But what is considered long-form content? Is an 800-word post enough, how about 1000 words or 3000 words?
To answer this we need to understand why long-form content performs better than shorter form content.
Search engines use your page copy to help extract the context of the page.
They look at both the words in your page, cross reference the semantics of those words and reference links internally and externally as well as reference the metadata in your images. Based on all of this data they determine what your page is about and rank it accordingly.
So the more content your page has the easier it is for Google to understand.
More than focusing purely on the length of your blog post, however, think instead about the content and its coverage.
Use modifiers in your titles.
Modifiers are added to your base keyword. Words like best, top, buy, and the year.
For example, someone might search for the term “best shoes”, but they might also search for “best running shoes” or even “best running shoes of 2018”
A great way to find modifier keywords that have real search volume is with Googles autosuggest feature.
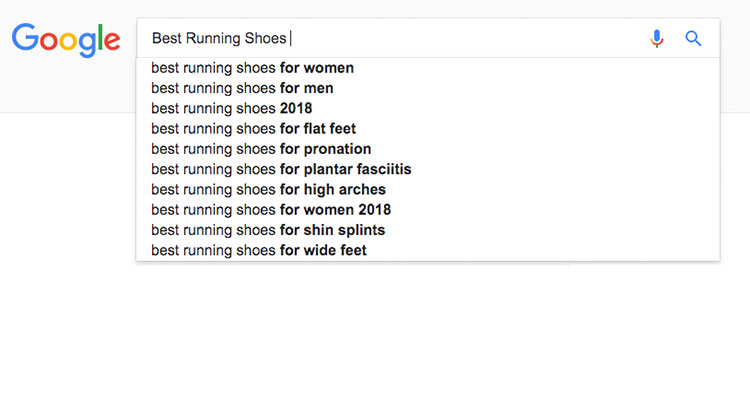
Simply type your keyword into Google then before hitting search, scan the terms that Google suggests in their results. These terms indicate popular search terms related to your primary keyword word.
Fast loading pages.
Back in 2010 Google announced that page speed would now be included as a signal in their search algorithm rankings. As of July 2018, Google has announced that page speed will become a ranking factor for mobile search as well.
Despite this, some studies show that optimizing especially for page speed has a minimal effect on rankings, but where it does factor in, is with usability which affects a whole host of things like bounce rate, time on site, etc.
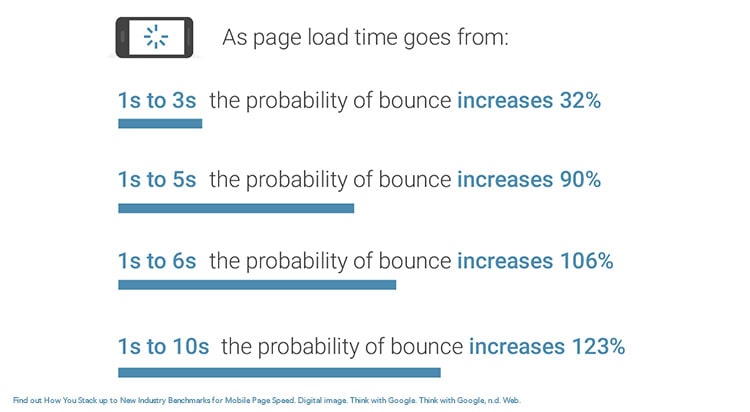
So how might you speed up your website?
Googles page speed insights tool.
First, you want to get a pulse for how fast your website is. A great way to measure this is with Googles page speed insights tool. This tool rates your websites speed and provides suggestions on how to improve upon that speed.
Use a content delivery network.
A content delivery network or CDN for short is a network of distributed servers that host versions of your website across multiple geographic locations. This improves the overall user experience for your end user by reducing the load time needed to fetch and pull your site up in a browser.
Image compression
Images in their original format can be quite large and reduce your websites load time. You can use an Online Image compressor tool like optimizilla to reduce your images sizes.
Use Caching.
Website caching allows your website’s data to be temporarily stored on a users browser so that the returning visitor can access your website’s data without pulling it back down from the website’s server.
If you your website is on WordPress there are a handful of useful caching plugins that can be easily integrated into your site.
Enhance your UX by improving your website’s users interface.
This last factor pretty much summarizes all of the previous tips into one. When you think about it Google’s job is to provide the best search experience to their users. The better their search results match users to relevant pages the more likely users are to continue to use Google as their primary search engine.
When you align your website with the incoming traffic search intent, you are playing into this ecosphere and are likely to see improved rankings as a result.
But user experience goes beyond just copy. Things like your websites design, layout and navigation also play a role.
Improved Readability
As mentioned early in this post on average users don’t read the content of a page in its entirety. This means that the more scannable your copy is the better experience the user will have.
Break up text with images. Add bullet points and bold and italicize portions of text that you want to have stand out to your readers.
Include supplemental multimedia content throughout your posts to keep users on a page longer. Things like embedded video, audio transcript, and supplemental infographics go a long way to keep users engaged and on your site longer.
Wrapping it all up.
So when evaluating what on page techniques to include in the content of your website remember, keep your URLs short, try to include your keyword in your URL , include your keyword your headline, don’t be afraid to link out to relevant pages, uses long-form content, use descriptive modifiers in your titles, and make sure your page load fast and copy is easy to scan through.
Considering all of these factors should put you in a position gain more visibility and perform better in the search engines.
